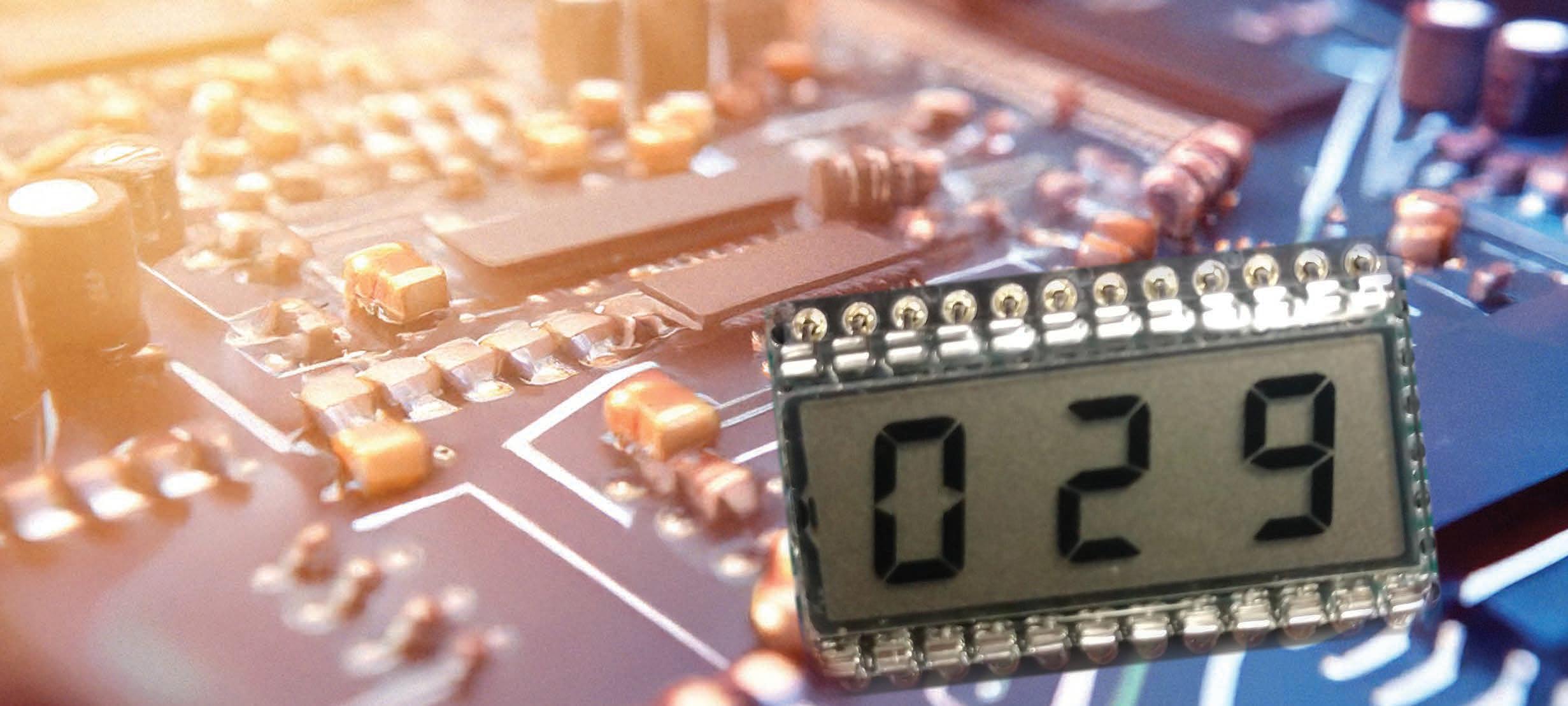
LCDs have displaced LEDs for many embedded systems and there are several reasons why OLEDs haven't completely taken over. Stuart uses a Lumex LCD with a Microchip driver for a TMC4 MCU to demonstrate the optimal setup. He then runs through some key criteria for selecting a display including customized options.
LCDs (liquid crystal displays) are used in a lot of modern electronics today. Most computer monitors and televisions are LCDs. Small embedded systems have LCDs. Although OLEDS have replaced LCDs in some applications, LCDs still find plenty of use.
LCDs have mostly displaced the older LED displays for alphanumeric information. LCDs are lighter, draw much less current, and can be read in conditions of high ambient light,such as sunlight. With a backlight, they can be read in low light or total darkness, although at the cost of increased power consumption.
We often use LCD modules with integrated controller ICs that provide a parallel, SPI, or I²C interface. An example would be the Lumex LCM-S01602DSF/C 2-line x 16-character alphanumeric display with a parallel interface.
High volume electronics often use LCDs without an embedded controller, the LCD module is soldered to the PCBA and controlled directly by the MCU, or by a controller that is in turn controlled by the MCU. An LCD without a driver is sometimes referred to as just the "glass".
OLED: What about OLEDS or Organic LightEmitting Diodes? An OLED uses more power than an LCD, but that's not really a fair comparison. A bare LCD is a reflective device, so it doesn't work well in low-light situations. An OLED is a lightemitting device, so it will work in low light. When you compare an LCD with an added backlight to an equivalent OLED display, the OLED may use less power. But this article is about LCDs.
LCD CONSTRUCTION
This story is from the December 2024 edition of Circuit Cellar.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the December 2024 edition of Circuit Cellar.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

New TI MCUs Enable Edge AI and Industry-Leading Real-Time Control to Advance Efficiency, Safety, and Sustainability
Texas Instruments (TI) introduced two new series of real-time microcontrollers that deliver advancements to help engineers achieve more intelligent and secure processing in automotive and industrial applications.

Using Amazon Alexa to Control Custom IoT Gadgets
In part two of his article, Brian describes integrating custom IoT gadgets with Amazon Echo using emulation to receive spoken alarms. In part one, he used emulation and Arduino Cloud services as a middleman.

Holiday Hangover Hardware Hacking
Having too much cheer during the holidays? In this month's article, Colin offers a diversion from the jolly season by urging developers to retreat to the basement to brush up on hardware hacking skills. He shows how a low-cost Raspberry Pi Pico and a TP-Link Tapo C200 smart IP camera could become the next automated bird deterrent or a home automation server.

Datasheet: Microamps Per Megahertz Ultra-Low Power MCUs Minimize Current Consumption
How do chip makers differentiate if many ultra-low power MCUs on the market feature the same processor core? The peripherals and different power states offer various ways to manage current consumption down to microamps per megahertz.

Smart Home Lock Down Matter Provides Security Blanket
As more devices in the smart home connect to the Internet, they become increasingly vulnerable to outside attacks. Developers can now add the latest security measures to their Smart Home devices through Matter.

Basic Pulse Circuits
In part one of a three-part series, Wolfgang wrote how basic pulse circuits help digital circuits, such as embedded boards with ARM processors, deal with pulse trains or bursts of pulses from the outside. In Part 2, he dives into enabling flip-flops, timing parameters, and synchronization, design tasks needed to capture, detect, and filter pulses.

Building a Wi-Fi Router Watchdog
Dev created a watchdog for a Wi-Fi extender using a Raspberry Pi Pico. This monitors Wi-Fi connectivity for his smart home lighting system, which would require a reset twice a year due to rapid power interruptions.

Create Your Own PCBs with a CNC Milling Machine
Using KiCad, CopperCAM, and Candle Software

Performance Bottlenecks in Embedded Linux Solutions Analysis, Identification, and Mitigation
Good performance is a requirement for every technology, and system designers rely on operating systems to ensure fast and smooth transitions in critical applications. Fortunately, Pedro writes, the embedded Linux OS offers ways for finding, analyzing and mitigating performance bottlenecks so embedded systems can deliver the speed and efficiency that end users expect.

Renesas New RA8 Entry-Line MCU Groups Brings High Performance of Arm Cortex-M85 Processor to Cost-Sensitive Applications with Market-Leading CoreMark Performance
Renesas Electronics Corp., a premier supplier of advanced semiconductor solutions, introduced the RA8E1 and RA8E2 microcontroller (MCU) groups, extending the industry's most powerful series of MCUs.