
Disaster could strike at any moment. For hundreds of millions of years, life on Earth has had to contend with a litany of existential threats: wayward asteroids, deadly pandemics, frigid ice ages and hellish volcanic eruptions. Today, the threat of climate change perhaps looms largest.
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, almost one in five land species have a high risk of going extinct by 2100 if global temperatures continue to climb unchecked.
The situation in the oceans is just as dire, as marine biologist Dr Mary Hagedorn, an expert on coral reefs from the Smithsonian's National Zoo, explains. "They're disappearing faster than we can save them." Her work focuses on cryopreserving coral, including its sperm cells and larvae, by using liquid nitrogen to store them in a deep freeze. "Once the material is properly cryopreserved, it's basically in stasis for all time," she says. One day they could be reintroduced to help stabilise ecosystems.
Her success has led Hagedorn to what might seem an outlandish proposal: a vault on the Mooncontaining alive-but-frozen samples of cells from the species most important in rebuilding ecosystems.
BURIED ON THE MOON
Could this plan actually work? Hagedorn points to the Global Seed Vault in Svalbard, Norway, inside the Arctic Circle, as an example. Currently home to over a million seed species, it's there to safeguard our food supply against catastrophic loss of some of the world's most important crops. It's a so-called 'passive repository', meaning it requires no people or energy to maintain the seeds at -18°C (-0.4°F).
But deep-freezing live cells requires a temperature below -196°C (-321°F), the boiling point of the liquid nitrogen used in cryopreservation. "There's no place on Earth cold enough to have a passive repository that can be held at -196°C," says Hagedorn, "so we thought about the Moon."
This story is from the September 2024 edition of BBC Science Focus.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the September 2024 edition of BBC Science Focus.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

THE WORST IDEAS OF THE 21ST CENTURY
NOT ALL IDEAS CAN BE HITS. ALONGSIDE GROUND-BREAKING INNOVATIONS, 21ST-CENTURY SCIENTISTS HAVE HELMED THEIR SHARE OF WILD TECH FLOPS, DUBIOUS THEORIES AND OVERHYPED BREAKTHROUGHS. HERE ARE THE BIGGEST TO FORGET

10 IDEAS THAT WILL SHAPE YOUR NEXT 25 YEARS
Predicting the future is considered a fool's game. But it's one many of us like to play.

THE BIGGEST BREAKTHROUGHS OF THE CENTURY
We're a quarter of the way into the new century. To mark this milestone, we asked the UK's top minds to highlight some of the game-changing scientific breakthroughs shaping our world since the year 2000

DO THE SCIENCE COGNITIVE SHUFFLE
Trouble sleeping? A lot on your mind? Use this trick and sedate your synapses
WHAT DETERMINES HOW MANY ABS I CAN GET?
Assuming you're a human being, you have exactly the same number of abs as everybody else: two.

HOW CAN I IDENTIFY MY PSYCHOLOGICAL BLIND SPOT?
In the 1950s two American psychologists, Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham, proposed a way of thinking about psychological blind spots - things you don't know about yourself - that they called the 'Johari Window' (the term is a combination of their first names).

How can I change my personality?
Want to become more confident, extroverted or assertive? Science shows that with a few simple changes, you can unlock your best self

Could your cosmetics be harming your health?
Cosmetic companies are phasing out microplastics and so-called 'forever chemicals' to help protect consumers.

extraterrestrial US Congress is talking about activity again. Is the truth really out there?
Despite several testimonies, the question remains frustratingly unanswered
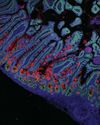
Map of 100 million human body cells revealed
Over three dozen new studies mark significant milestone towards complete Human Cell Atlas