
In the context of mental health, a phobia is far more serious than a mild aversion.
Many of us dislike flying, or giving a talk in front of our colleagues, and we might not be too happy if a large, slobbery dog, no matter how gentle, came bounding toward us. But as long as we can tolerate these kinds of situations without too much distress, and our lives aren't adversely affected, then we haven't got a phobia for any of these situations as such.
In contrast, people diagnosed with a relevant phobia would experience an intense, extremely unpleasant fear reaction that could be overwhelming. So much so, that it might interfere with their day-to-day lives. Flying phobias, social phobias, and a fear of dogs (even cute ones) are common examples - but there are dozens of others, including some quite bizarre examples, such as trypophobia, which is a fear of clusters of holes (like you get in crumpets), sedatephobia (a fear of silence) and gerascophobia (a fear of ageing).
ARE PHOBIAS A DISORDER?
Phobias are a formal psychiatric diagnosis in the anxiety category. To be diagnosed, you'd need to have experienced a phobia for at least six months, and your fear reactions to the focus of your phobia would need to be out of proportion to the danger you were in.
Psychiatry recognises five main categories of 'specific phobia' (between 3 to 15 per cent of people will develop one of these at some point in their lives): animal phobias (spiders and snakes are common examples); environmental phobias (such as heights or deep water); blood/injection phobias (think needles or the mere sight of blood); situational phobias (such as bridges or dentists); and finally an 'other' category that covers almost everything else, such as a fear of swallowing or being sick.
This story is from the April 2023 edition of BBC Science Focus.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the April 2023 edition of BBC Science Focus.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

THE WORST IDEAS OF THE 21ST CENTURY
NOT ALL IDEAS CAN BE HITS. ALONGSIDE GROUND-BREAKING INNOVATIONS, 21ST-CENTURY SCIENTISTS HAVE HELMED THEIR SHARE OF WILD TECH FLOPS, DUBIOUS THEORIES AND OVERHYPED BREAKTHROUGHS. HERE ARE THE BIGGEST TO FORGET

10 IDEAS THAT WILL SHAPE YOUR NEXT 25 YEARS
Predicting the future is considered a fool's game. But it's one many of us like to play.

THE BIGGEST BREAKTHROUGHS OF THE CENTURY
We're a quarter of the way into the new century. To mark this milestone, we asked the UK's top minds to highlight some of the game-changing scientific breakthroughs shaping our world since the year 2000

DO THE SCIENCE COGNITIVE SHUFFLE
Trouble sleeping? A lot on your mind? Use this trick and sedate your synapses
WHAT DETERMINES HOW MANY ABS I CAN GET?
Assuming you're a human being, you have exactly the same number of abs as everybody else: two.

HOW CAN I IDENTIFY MY PSYCHOLOGICAL BLIND SPOT?
In the 1950s two American psychologists, Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham, proposed a way of thinking about psychological blind spots - things you don't know about yourself - that they called the 'Johari Window' (the term is a combination of their first names).

How can I change my personality?
Want to become more confident, extroverted or assertive? Science shows that with a few simple changes, you can unlock your best self

Could your cosmetics be harming your health?
Cosmetic companies are phasing out microplastics and so-called 'forever chemicals' to help protect consumers.

extraterrestrial US Congress is talking about activity again. Is the truth really out there?
Despite several testimonies, the question remains frustratingly unanswered
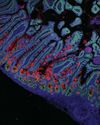
Map of 100 million human body cells revealed
Over three dozen new studies mark significant milestone towards complete Human Cell Atlas