
While it's been disappointingly quiet for comet observers, aurora hunters and meteor watchers, there's no doubt that 2022 has been a great year for planet spotters. Back in early summer there was a striking and much-hyped 'chain of worlds' spread out across the sky, with half a dozen planets strung out along the ecliptic like beads on a bracelet. Unfortunately, that celestial treat was only visible before dawn, so many people missed it or didn't even know it was happening at all.
But good news: another planetary parade will be on view this month! And even better news: this time it will be in the evening sky, so you won't need to set the alarm really early to see it. Throughout September no less than five planets - Saturn, Jupiter, Mars, Uranus and Neptune - will all be on view at once, if you look at the right time.
As exciting and rare as it was, summer's planetary line-up wasn't easy to see for many Northern Hemisphere sky-watchers - some of the planets were overwhelmed by the bright summer sky. But this month's gathering will be taking place after dark, so all the planets involved will be either very easy to see with the naked eye or easy to find in binoculars and small telescopes. And as an added bonus, one of the Solar System's most famous minor planets, Vesta, will be in the same region of the sky too.
But when will be the right time'? Although some of these worlds will be on view soon after sunset, you won't be able to see all of them strewn across the sky together until around 10:30pm, so if you want to show them to any space-mad youngsters, they may need to take a nap first and then go out later. We'll look at the view on one particular night mid-month, 18 September, but don't worry if it's cloudy on that night because these planets will be on view throughout September.
This story is from the September 2022 edition of BBC Sky at Night Magazine.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the September 2022 edition of BBC Sky at Night Magazine.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

Could We Find Aliens by Looking for Their Solar Panels?- Designed to reflect ultraviolet and infrared, the panels have a unique fingerprint
Researchers searching for life beyond Earth spend a lot of time thinking about what telltale signs might be detectable astronomically. Forms of unambiguous evidence for the presence of life on another world are known as biosignatures. By extension, techno signatures are indicators of activity by intelligent, civilisation-building life.

Antimatter- In our continuing series, Govert Schilling looks at antimatter, the strange counterpart to most of the matter filling our Universe
Particles and corresponding antiparticles are very much alike, except they have opposite electrical charges. For instance, the antiparticle of the electron - known as the positron - has the same tiny mass, but while electrons carry a negative electrical charge, positrons are positively charged.

Where Have All The Milky Way's Early Stars Gone?- Our Galaxy has a curious lack of pristine stars
The Big Bang produced a Universe filled almost exclusively with hydrogen and helium; all other elements - what astronomers call metals - were produced by stars, supernovae and everything that happens later. So if you can pick out a pristine star with no metals polluting it from among the billions in the Milky Way, then you are likely to have a star dating from our Galaxy's earliest days.

Inside The Sky At Night - Two years ago, exoplanet scientist Hannah Wakeford received some of the first data from the JWST
Two years ago, exoplanet scientist Hannah Wakeford received some of the first data from the JWST. In July's Sky at Night, we discovered what she's learned since then.

How to stack DSLR data in Siril
Easily combine multiple frames to boost detailin your astro photos
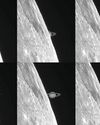
Lunar occultation of Saturn
You'll need to strike a balance on 21 August to capture the Moon covering the ringed planet
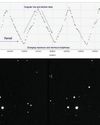
How to plot a variable star light curve
A rewarding project to chart stars that change brightness

Smartphone photography with a telescope
Mary Mcintyre explains how to get impressive night-sky images using your phone

Once-a-century solar storm is overdue
If a Carrington Event struck today it would be catastrophic, says Minna Palmroth

The new era of human spaceflight
There's been a step-change in crewed space missions since the dawn of the 21st century. Ben Evans charts its course and looks ahead to future horizons