
Researchers created a database of over 87,000 games spanning the course of 26 years in European soccer leagues between 1993 and 2019. For simplicity, they chose to eliminate tied games.
Factoring in things like strength of schedule, for each new match they used a logistic regression algorithm a classification algorithm that helps assign data into discrete buckets, like labeling emails as either spam or not spam-to predict the probability of their match's outcome. Researchers found a clear difference between the predictability of games played 10 years ago and matches played today. In a German league, for example, the model has an accuracy of 60 to 65 percent in the early 2000s, and 80 percent accuracy with data from the late 2010s.
This story is from the September - October 2022 edition of Popular Mechanics US.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the September - October 2022 edition of Popular Mechanics US.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 9,000+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In

ONE OF THE 'GREATEST THREATS' TO THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST ISN'T WHAT YOU THINK.
EXPERTS ARE PREPARING THE REGION AGAINST THE THREAT OF DANGEROUS VOLCANIC MUDFLOWS, KNOWN AS LAHARS, WHICH COULD INUNDATE THE COMMUNITIES SURROUNDING MT. RAINIER IN AS LITTLE AS 30 MINUTES.

THE WORLD'S TOUGHEST ROW
They rowed 3,000 miles across the Atlantic, battling unpredictable weather, chaotic seas, and finicky equipment. But what they discovered gave them profound new insights into the power of the ocean.

HOW TO DIY OFF-GRID SOLAR
SPEND THE TIME UP FRONT AND PLAN IT CAREFULLY TO AVOID DISAPPOINTMENT
Are We on the Verge of an ARMS RACE in SPACE?
RUMORS OF A RUSSIAN SPACE NUKE, ALONG WITH OTHER SATELLITE-TARGETING WEAPONS, HAVE MADE GEOPOLITICAL TENSIONS EXTEND INTO ORBIT.

Fresh Fingerprints on an Ancient Statue
A CLAY FIGURINE HAS SPENT MILLENNIA incomplete, waiting at the bottom of a lake for its long-dead craftsman to finish the Iron Age-era statuette.

Quantum Entanglement in Our Brains
IT HAS LONG BEEN ARGUED THAT THE human brain is similar to a computer. But in reality, that's selling the brain pretty short.

The Tools of Copernicus
WAY BACK IN 1508, WITH ONLY LIMited tools at his disposal, Nicolaus Copernicus developed a celestial model of a heliocentric planetary system, which he described in hist landmark work De revolutionibus orbium coelestium. It was a complete overhaul of our conception of the universe-one that, unfortunately, earned him the ire of the Catholic church for decades after his death-and forever changed the way we look at the stars.

Building a Sixth-Generation Bomber Raptor
THE GLOBAL COMBAT AIR Programme (GCAP)-a project by the U.K., Italy, and Japan to develop a sixth-generation stealth fighter-has been busy at the drawing board reshaping its vision of the future of air warfare. And judging by the new concept model unveiled at this year's Farnborough air show, that future has big triangular wings.

The Electroweak Force of the Early Universe
TODAY, THE UNIVERSE AS WE KNOW IT IS governed by four fundamental forces: the strong nuclear force, the weak nuclear force, electromagnetism, and gravity.
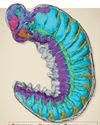
This Ancient Fossil With a Brain and Guts
WE KNOW WHAT FOSSILS LOOK like. For example, typical dinosaur fossils are bones turned to stone and preserved from the passage of time, located, if we're particularly lucky, in large collections that can be reassembled to represent the beast they used to prop up in their entirety.